caydieu
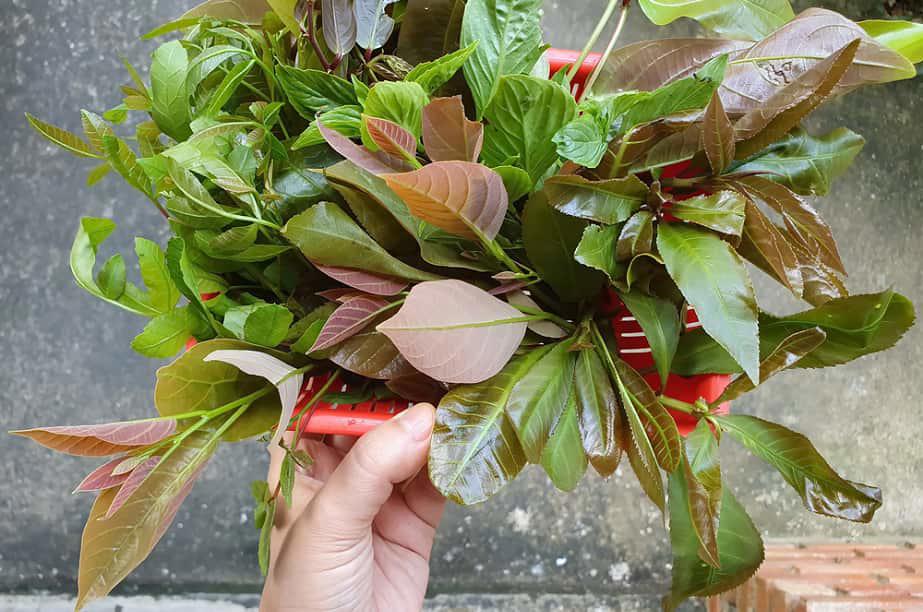

Cashew leaves - Features, nutritional values and applications
In Vietnam, there are a lot of supplies of cashew leaves. However, the applications of cashew leaves have not been exploited and left a lot of potential. So what are the characteristics and applications of cashew leaves?
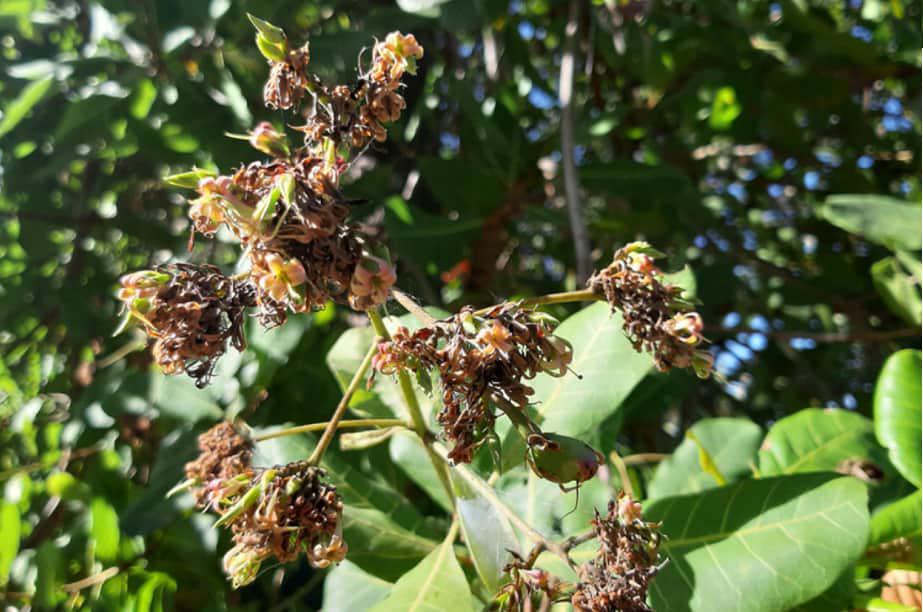

Diseases of cashew nut plants - Inflorescence blight, anthracnose, damping off, die-back (pink disease), leaf spot disease, sooty mould
Inflorescence blight symptoms are characterized by water-soaked areas appearing on primary or secondary branches resulting in drying up the flower stems. From these small wounds, the sap exudes and turns pinkish-brown within 1 day, enlarges and coalesces in 2-3 days.
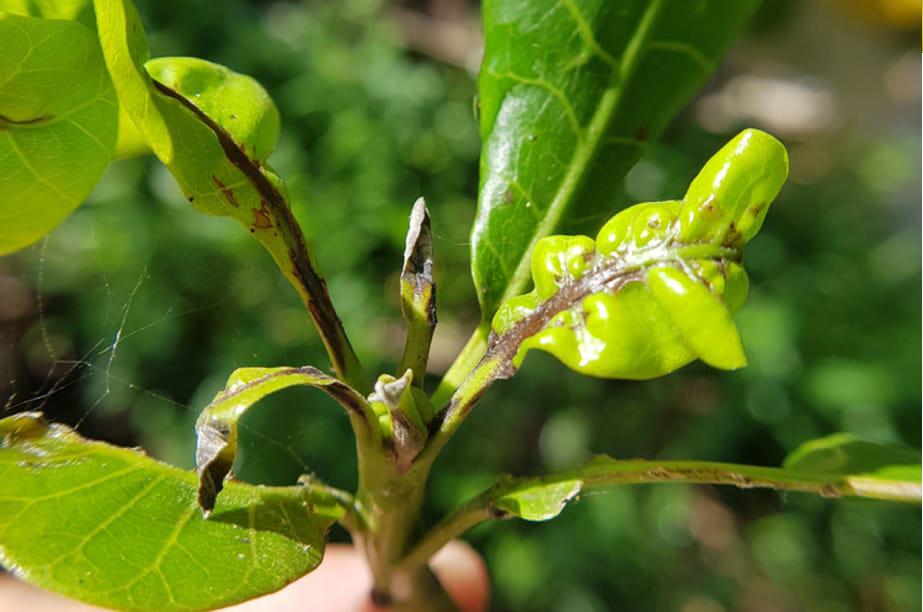

Pests of cashew nuts - Tea mosquito bugs, stem and root borers, leaf miners, leaf and blossom webbers, bud borers, bagworms, red caterpillars, green weevils
Cashew nut plant, as well as other crops, is attacked by many insects and fungi separately or in combination, causing many different diseases for the tree and serious damage to production and sometimes death to the whole plant.
-1.jpg)
Propagation of the cashew tree by vegetative methods - Layering & Grafting
Asexual propagation is accomplished through cell division. In which, the chromosomes and cytoplasm of the mother cell divide to produce two daughter cells. The plants created by this propagation method, therefore, will carry a combination of traits and genes of the mother plants, which is the reason why selection of mother plants must be done carefully.
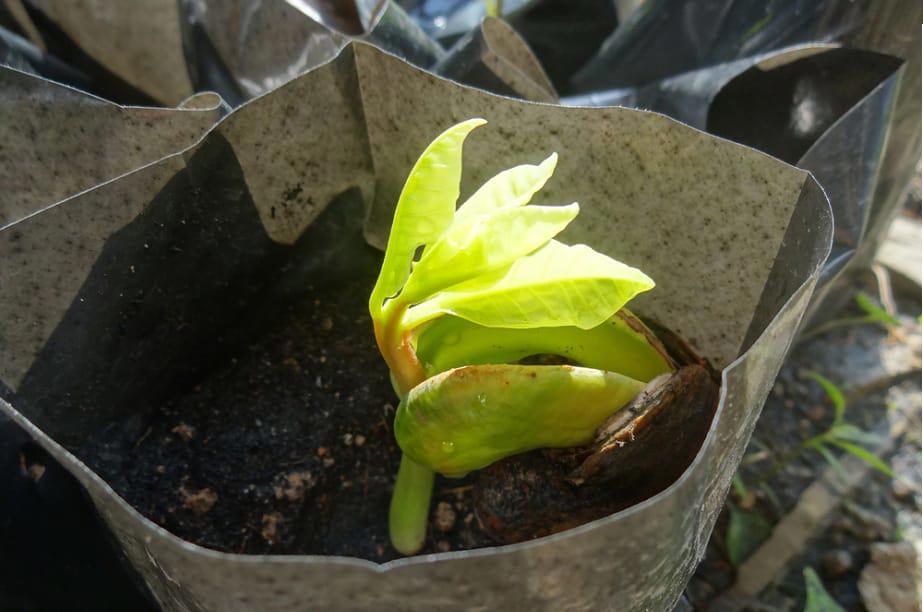

Sexual propagation of cashew (through seeds)
Multiplication of cashew plants by sexual method through directly sowing seeds is one of the methods of creating freshly cashew trees.

Cashew fruit, roots, stems, leaves, sap and bark
Planting cashew trees is mainly for the purpose of producing cashew nuts. Large amounts of cashew nuts are currently considered agricultural waste and by-products of the cashew nut production process. Cashew fruit (scientific name is Anacardium Occidentale L.) is a multi-purpose fruit.

Botanical description of the cashew tree
The cashew tree is a woody tree, growing to between 8 and up to 12 meters tall, with a canopy diameter of 10-12 meters. In excellent soil and climate conditions, it can grow up to 20 meters high.

Cashew care: weeding, pruning, creating canopy, watering, fertilizing, renovating old gardens
Cashew care plays a very important role in maintaining the growth and the high yield of the cashew tree. Care includes tasks such as weeding, pruning, creating the canopy, irrigation, fertilizing and renovating old cashew gardens.
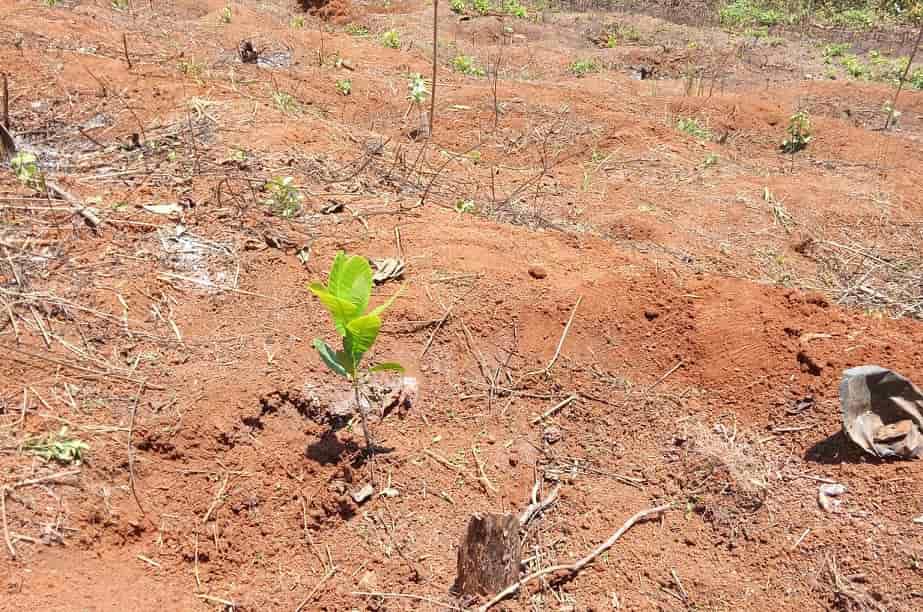

Cashew plantation: land preparation, planting space, digging planting pits and intercropping
For a long time, the cashew tree was only considered a natural and semi-natural tree and was not cared for thoroughly like other crops. The yield of products obtained from the cashew tree were almost ignored because they were considered as a natural gift given by God.

Cashew Varieties
Like other crops grown from seeds, the cashew tree is a highly cross-pollinate and widely spreading crop. Thus, it is easy to see the diversity of a cashew population.
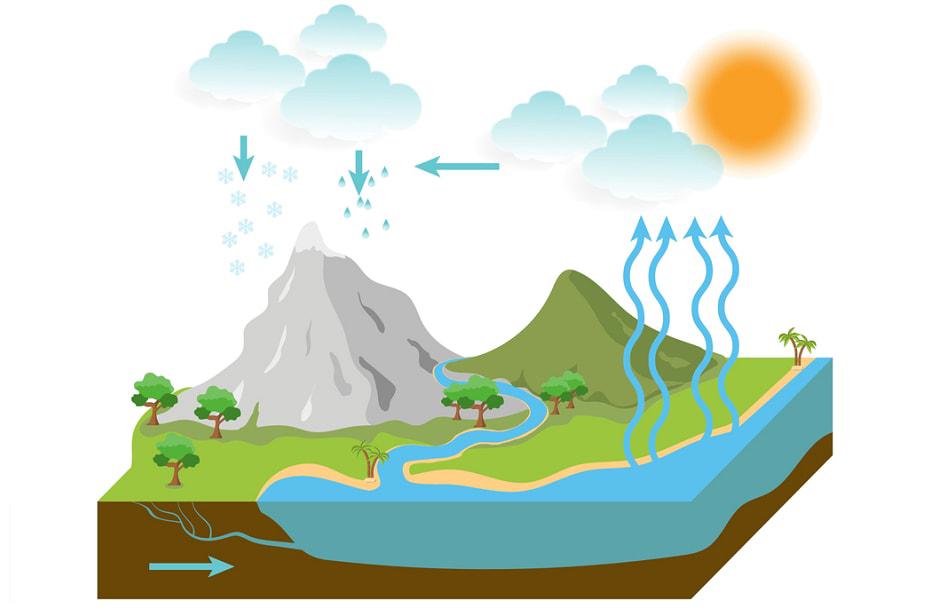
Cashew - Climate, Soils And Nutrients
Cashew trees can tolerate in places with diverse and harsh climatic conditions. Cashew grows best in the tropical climate, with sufficient annual rainfall and a well-defined dry season. The tree loves high temperatures, and is very sensitive to cold.
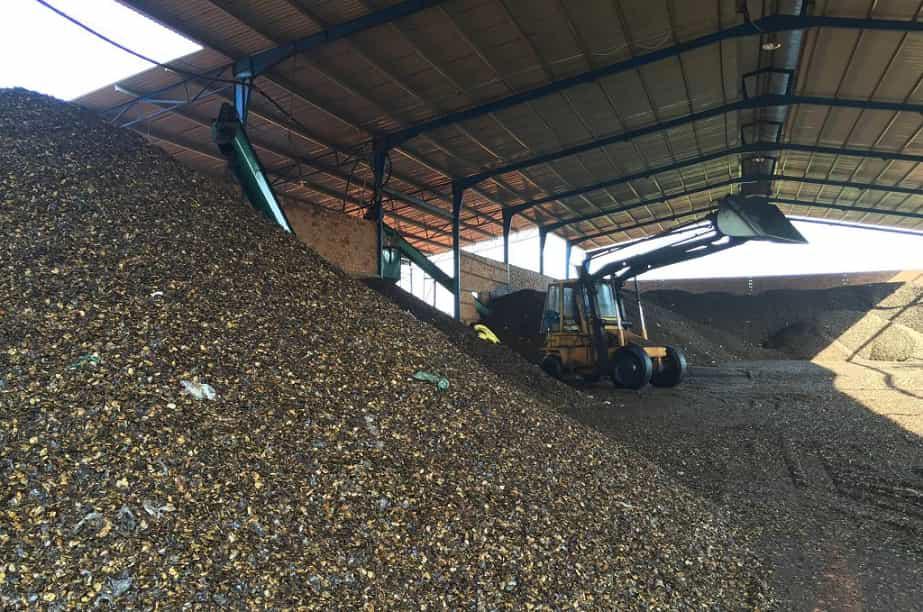

Cashew Nut Shell Oil, Cashew Nut Shell Charcoal, Cashew Testa Skin and Cashew Wood
Cashew shell is what many people consider junk, but is becoming a new source of raw materials with many applications and could open up a market of hundreds of millions of dollars, positively contributing to the value chain of the cashew industry.