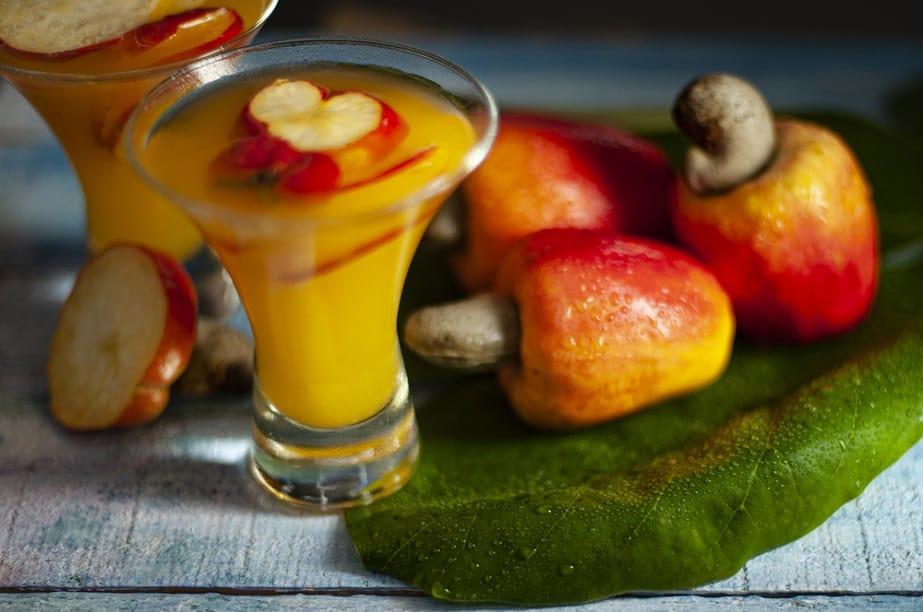
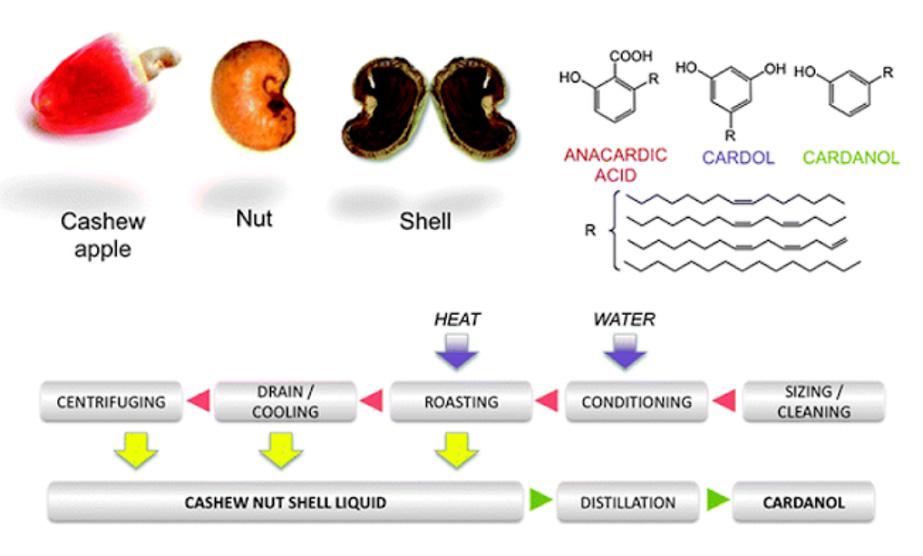
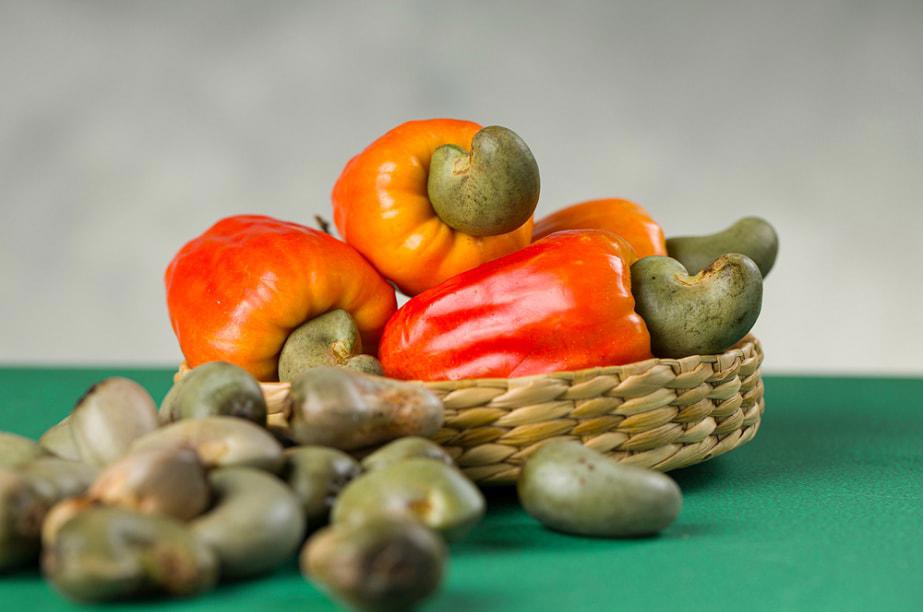
Cashew fruit
Planting cashew trees is mainly for the purpose of producing cashew nuts. Large amounts of cashew nuts are currently considered agricultural waste and by-products of the cashew nut production process. Cashew fruit (scientific name is Anacardium Occidentale L.) is a multi-purpose fruit. Cashew nuts can be processed as food for humans. In addition, they are also raw materials for many industries and have many applications in medicine.
Nutritional content of cashew fruit
Table 1. Nutritional ingredients in 100g of cashews
|
Ingredients |
Nutritional content |
|
Moisture content |
86.3% |
|
Energy |
51 kcal |
|
Protein |
0.2 g |
|
Fat |
0.1 g |
|
Fibre |
3.2 g |
|
Carbohydrates |
11.1 g |
|
Minerals |
0.8 g |
|
Calcium |
10 mg |
|
Iron |
0.2 mg |
|
Riboflavin |
0.05 mg |
|
Thiamine |
0.02 mg |
|
Niacin |
0.3 mg |
|
Phosphorus |
67 mg |
|
Carotene |
23 micrograms |
|
Vitamin C |
180 mg |
Table 2. Chemical composition and nutritional value in cashew fruit
|
Composition |
Detailed composition |
Value range |
References |
|
Sugar |
Total sugars ( maltose, sucrose, raffinose and two higher) |
6.3 – 9.9 g/100 g |
Azoubel et al. (2005) |
|
Reducingsugars ( fructose và glucose) |
6.24 – 9.8 g/100 g |
Damasceno et al. (2008) |
|
|
Vitamins |
Vitamin C |
126 – 372 mg/100 ml |
Damasceno et al. (2008); Morton and dowling (1987); Gunjate and patwardhan (1995)]; Price et al. (1975) |
|
Minerals |
Ca, P, Fe, K, |
0.9 - 21.4 mg/100 g |
Osho (1995) và Morton and Dowling (1987) |
|
Mg, Zn, Na |
1.53 g/L 16 – 105 g/L |
||
|
Amino acids |
0.88 - 3.36mM |
Oliveira et al. (2002) |
|
|
Polyphenols |
Axit Gallic, axit protocatechuic, |
215.1 – 412.8 |
Lowor và Agyente-Badu (2009) |
|
β-cryptoxanthin, zeinoxanthin, lutein |
mg/100 ml |
||
|
Organic acids |
Axit Malic, axit citric, axit lactic |
0.1 – 0.36 g/100 ml |
Joseph (2010) và Price et al. (1975) |
|
Tannins |
0.22 – 0.58 g/100 ml |
Price et al. (1975); Gunjate và patwardhan (1995) |
|
|
Proteins |
Protein |
0.1 – 1.04 g/100 g |
Price et al. (1975); Osho (1995) |
|
Carotene |
0.03 – 0.74 mg/100g |
Morton and Dowling (1987) |
|
|
pH |
3.67 – 4.53 |
Gunjate and patwardhan (1995); Osho (1995) |
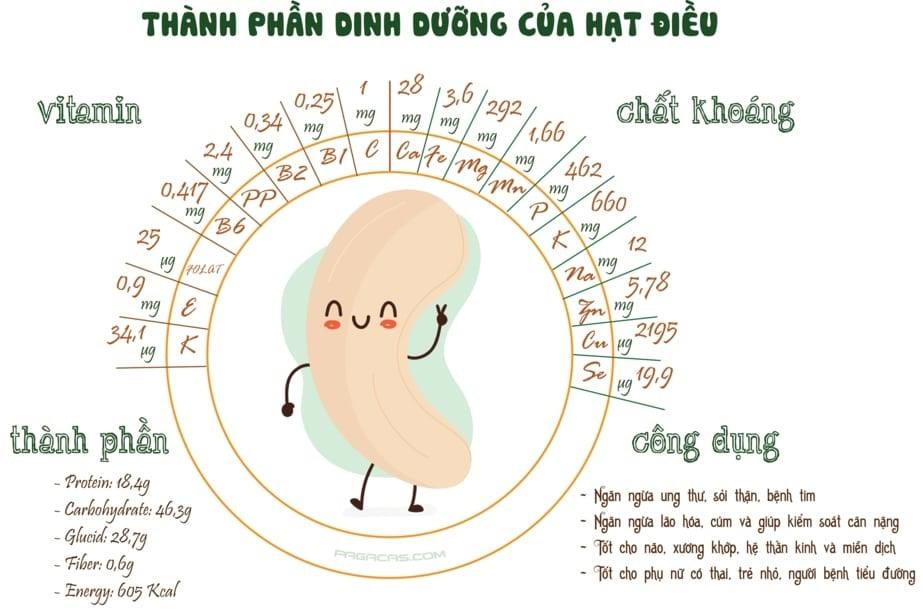
Cashew fruit is considered a nutrient-rich fruit. The average content of vitamin C in 100g of cashew fruit stands at 180mg (Table 1), which is very high, much higher than the vitamin C content in other citrus fruits such as grapefruit (95 mg), orange (40 mg), lemon (40 mg) (according to Vietnam Food Composition Table, Medical Publisher).

Besides, there are many necessary minerals for the body in cashew nuts such as Ca, P, Fe, K, Mg, Zn, Na. Cashew fruit also contains many amino acids, protein and a moderate amount of sugar (Table 2). In particular, cashew fruit is also very rich in polyphenols - antioxidant compounds that are very good for human health.
However, there is just a limit - cashew nuts contain Tannins - a compound belonging to the polyphenols group but often causes an astringent taste. This compound is often found in green tea and is considered a beneficial compound for health.
Uses of cashew fruit
- Used as food for humans
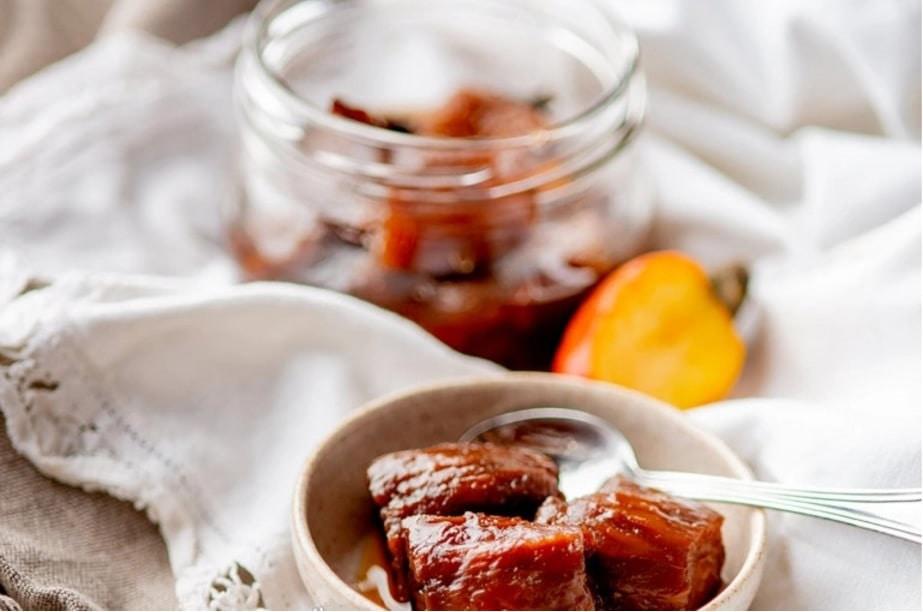
Cashew nuts have long been used as food for humans because of their diverse nutritional content. Ripe cashew nuts can be instant and have a sweet, aromatic taste along with a distinctive astringent taste after eating. Besides, in Vietnam, ripe cashew nuts are also considered as a topping (sliced cashew nuts horizontally or vertically, star fruit, astringent bananas, Malabar vegetables, etc.) for several salty dishes such as braised meat and fish, sour cashew soup, cashew fruit salad.

- Used to make medicine
Traditionally, cashews are used to treat a number of chronic diseases such as Scurvy (a chronic disease caused by vitamin C deficiency), diarrhea, uterine problems, dropsy, cholera and rheumatism (Attri 2009) [3]. Cashew nuts are also considered a cure for stomach disorders and sore throats in Cuba and Brazil. In Bolivia, they are considered a human brain stimulant that helps improve memory. Also, they are also used as a strong diuretic. Besides, because of cashews’ beneficial ingredients such as antioxidant, anti-fungal, antibacterial, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory and anti-mutation, many properties of cashew juice have been researched to apply their value in medical treatment.
In Vietnam, cashew fruit is used as a medicine with diuretic and anti-nausea effects. It can also be used to treat sore throats by drinking cashew juice.
In addition, according to some foreign research documents, ripe cashew nuts have been spread around water reservoirs by African people to limit the development of mosquitoes thanks to their ability to prevent the development of mosquito larvae of some acids contained in cashew fruit.
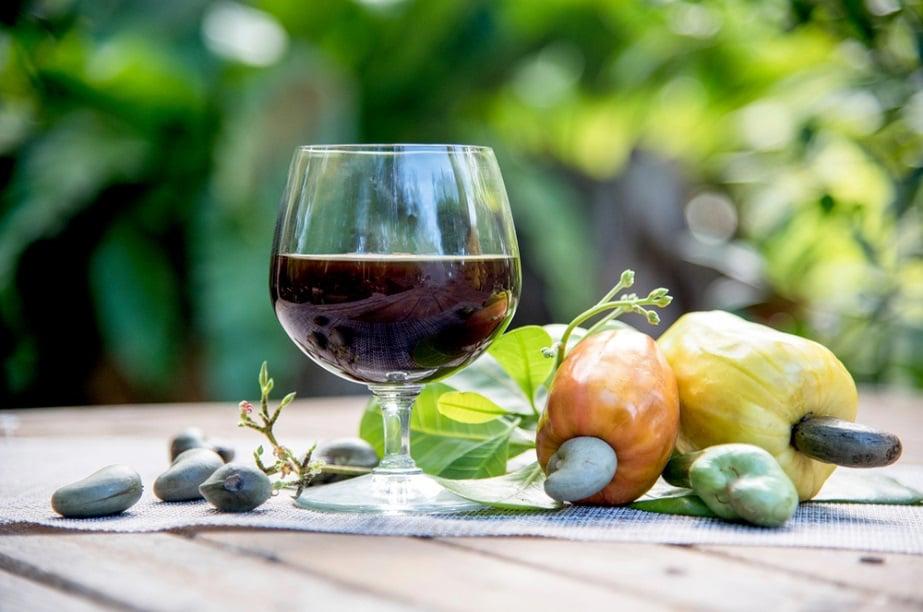
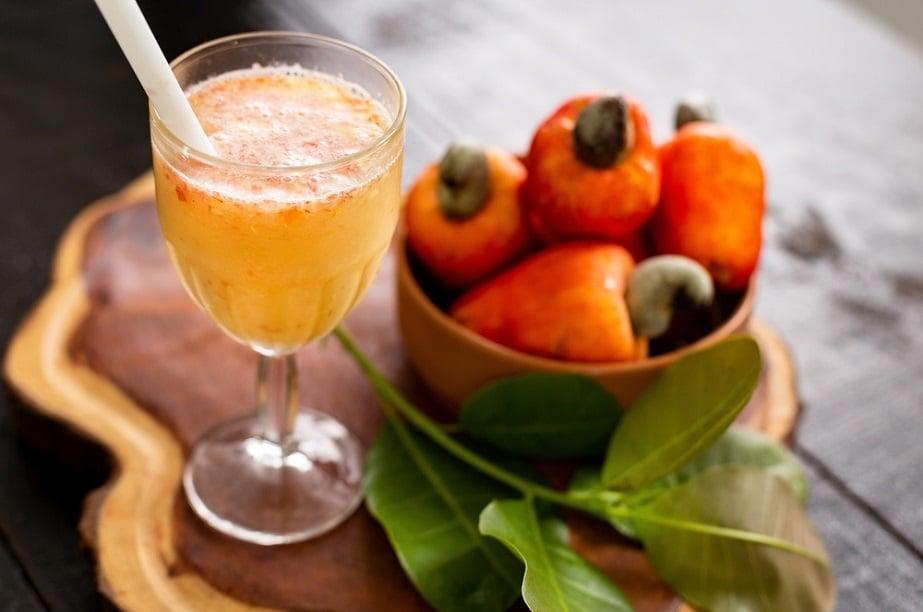
- Used to make wine and soft drinks
Cashew fruits have long been used to make wine and soft drinks. In India, the cashew wine industry has a tradition of more than 500 years while in Vietnam, the processing technology of the cashew wine industry has been researched and transferred to many businesses and family businesses. According to the Vietnam Union of Science and Technology Associations VUSTA, for every 1 kg of cashew fruit, 1.5 liters of cashew wine can be produced with an alcohol content of 11-13.3%.
Furthermore, the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology have removed tannins that cause acrid taste and burning tongue in cashew fruits successfully, thereby cashew fruits have been applied more in the beverages industry.
- Used to make dry alcohol, fertilizer and biofuel
Several ingredients are very suitable for the dry alcohol processing industry.In terms of processing, the juice from the cashew fruit will be added with Gelantine, then boiled and filtered to get the liquid. Next, add yeast (called Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and after 5 days, distill this solution to obtain alcohol. The final step is adding additives to obtain complete alcohol. The remaining fruit pulp can be composted to make biofertilizer.
Obtained dry alcohol can be used to produce finished products such as medical alcohol, hot pot cooking alcohol, etc. Especially, this type of dry alcohol can be used to produce anhydrous alcohol 99.8% - raw materials for mixing E10 biofuel, as a source of raw materials for the production of bioethanol and E10 base gasoline.
- Used to make animal feed
Cashew fruits are rich in protein, sugar and fiber, and contain a lot of vitamins, therefore, they are very convenient for the silage fermentation process to make animal feed, helping to supplement and partially replace forage from plants.
After harvesting and separating the nuts, fresh cashew nuts will be dried, then fermented or ground into powder to make food for cows. According to the analysis, the finished product has a very high nutritional content. Specifically, 33.17% crude fiber, 8.29% minerals, 6.1% protein and 1.29% fat. In fact, cows will grow faster in both weight and height, and the quality of meat and milk will also be better when supplemented with this type of food. Therefore, cashew nuts are very good raw materials for making animal feed and achieve high economic efficiency thanks to low costs.
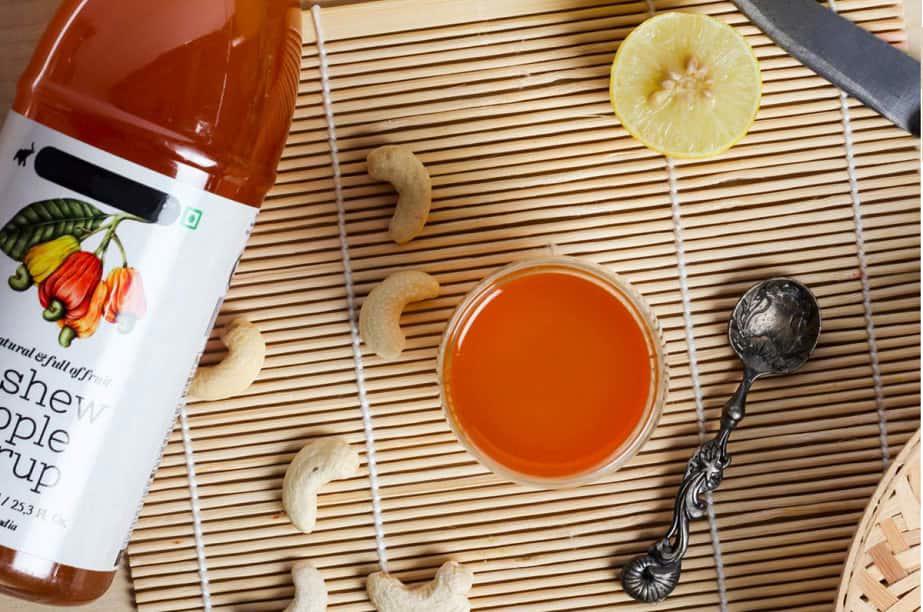
- Used to produce vinegar
According to VUSTA, for every 1.4 kg of cashew nuts, 1 liter of vinegar can be produced with a total cost of about 2,700 VND. Cashew vinegar is highly appreciated because cashew fruit contains good nutritional content. For the best result in the production process of vinegar, the vinegar should be fermented since the cashew fruit juice has fermented and reached a concentration of 7% and an appropriate pH of 3.5. It is necessary to add about 15% of vinegar and ferment for 25 days to obtain the final product of vinegar.
Cashew leaves
Although cashew leaves are rarely mentioned, they have many very useful applications in daily life. Some benefits can be mentioned as follows:
- Used as food: Citizens often used young leaves as raw vegetables. They are acrid mildly and are fragrant similar to fig leaves, so they are often used as raw vegetables or can be eaten with rustic dishes that are very familiar to Southern people such as snake meat, rat meat, shrimp soup.
- Used to make medicine: According to Sokeng's research, cashew leaves have recorded positive results in helping lower blood sugar. Cashew leaves contain many ingredients such as tannins, carbohydrates, saponins, flavonoids and alkaloids that have antioxidant, antibacterial effects, helping control diabetes. In addition, thanks to the ability to improve tissue activity through reducing glucose absorption in the intestine and increasing insulin production, cashew leaves have shown the effect of preventing hyperglycemia.Also, extracts from cashew leaves also help reduce the risk of complications in diabetics.
- Used to make fertilizer: after falling from the branches, cashew leaves are now mostly used to compost into natural fertilizer, thereby adding nutrients to the cashew tree itself.

Rễ, vỏ thân cây và nhựa thân cây điều
Roots, bark and sap
- Cashew roots: In India, cashew roots are used as an enema to treat constipation.
- Cashew bark: The cashew tree stem is covered by a rough and hard shell. This shell contains 4.7% astringent substances, so it is used in the preparation of fabric dyes and leather tanning drugs, and printing ink production.
- Cashew tree sap: Old cashew trees, after many years of growth, often secrete a sap with antiseptic properties. This type of plastic has high adhesive properties so it is used to produce glues, polishing varnishes in the wood industry, etc.
REFERENCES
- Table 1: C. Gopalan, Nutritive Value of Indian Foods;
- Table 2: The Pharma Innovation Journal 2017; 6(7): 260-264;
- Ks. Chinh N. M. và Dr. Nghia N. D., Trồng - Chăm sóc và phòng trừ sâu bệnh cây điều. Agricultural Publisher.
- Available at several links:
https://www.vinmec.com/vi/tin-tuc/thong-tin-suc-khoe/dinh-duong/tannin-trong-tra-la-gi-va-chung-co-loi-ich-gi/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tHcXNECH2ls
https://tuoitre.vn/cong-dung-lam-thuoc-cua-qua-dieu-113712.htm
https://www.businessinsider.com/feni-cashew-fruit-juice-liquor-goa-india-2021-6
http://www.vinacas.com.vn/lam-nuoc-trai-cay-va-ruou-tu-qua-dieu-bv1349.htm
http://vusta.vn/chitiet/tin-tuyen-sinh-dao-tao/San-xuat-ruou-vang-tu-trai-dieu-Hien-thuc-va-tuong-lai-1011
https://skhcn.binhphuoc.gov.vn/chu-%C4%91e-thong-tin-chuyen-nganh/ung-dung,-chuyen-giao-tien-bo-kh-cn/san-xuat-con-kho-tu-dich-trai-%C4%91ieu.aspx
http://vusta.vn/chitiet/tin-tuyen-sinh-dao-tao/San-xuat-giam-an-tu-trai-dieu-1011
https://ondinhtieuduong.com/tri-tieu-duong-bang-la-dieu/
https://caytrongvatnuoi.com/cay-lay-hat/loi-ich-cua-cay-dieu